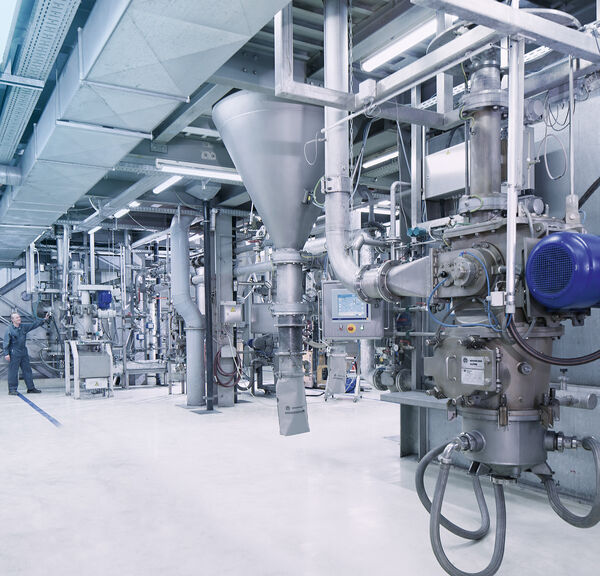
Para procesamiento de sólidos
Recambios y reparaciones
Control de procesos
Remote service
Comprobación de seguridad
Más información
Para instalaciones de película soplada
Recambios y reparaciones
Limpieza del cabezal de soplado
Remote-service/eSupport
Más información
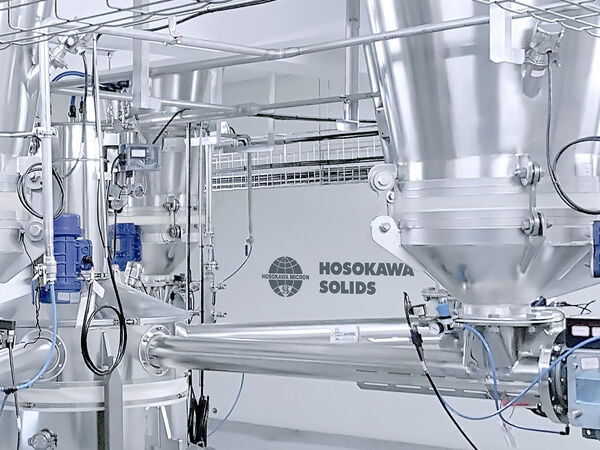
Hosokawa Solids pertenece al Hosokawa Alpine
Tu sólido a granel. Nuestra solución.Tecnología de transporte neumático, pesada y dosificación, así como silos equipados: desde 2020, Hosokawa Solids y sus componentes y sistemas forman parte del grupo Hosokawa Alpine. Ahora también puede encontrar la gama completa de Hosokawa Solids en nuestro sitio web.